

We have also seen what role it plays and how effective it handles its responsibility while the communication is targeted. We have seen the communication protocols structure (IPv4) and where ARP (the title of the article) lies in the communication protocol. The IP address of the device is on the receiving end.įinally, we are at the concluding statement regarding the discussion e had in this article on ARP. The hardware address of the device which is receiving the message The IP address of the device which is sending the message other values are being defined have a look at the below-mentioned table – OpCodeĭeals with the hardware address of the device that is sending the message This field demonstrates the nature of the ARP message. This specifies how long will the protocol address is going to be in the message. This is there to specify the length of the hardware relates addresses that are there in the message.
#Arp storm ddos tool code
For IPv4, the value is 2048, which also corresponds to the Ether code for the Internet Protocol. This is a compliment for the Hardware type field, specifying the type of layer being used in the messages. ARP Packet DiagramĮxplain in Detail: Components of ARP Packet Format FIELD NAME
#Arp storm ddos tool update
The last thing to perform before a successful connection is that the source machine will update its ARP cache with the sender hardware address and sender protocol address from the ARP reply message. The source machine will process the ARP reply from its destination and store the ‘Sender hardware address’. Now the destination device will update its ARP cache as it needs to contact the sender machine to establish a connection. Here the targeted device takes the ‘Sender hardware Address’ and ‘Sender Protocol Address’ from the ARP message and uses these values for the targeted hardware and protocols. If the findings happen, an ARP message is generated. If there is no match, then it will be dropped then and there itself without any actions. One thing to note is that here the ‘Target hardware address’ will be left blank as the machine is trying to find out that the source also broadcasts the ARP message request to its local network.īoth the device after this starts to compare the target protocol address with its protocol address.
#Arp storm ddos tool plus
If the MAC address is present in the resolved state, then it will utilize that MAC address to establish the communication.īut if the resolved ARP is not there, then the source machine will create the ARP request message and put its datalink address plus its IPv4 address as sender protocols address.

The first thing to do in those processes would be for the source device will check its ARP cache and finds out if it has a resolved MAC address for the destination device or not. So, these two want to communicate between them.
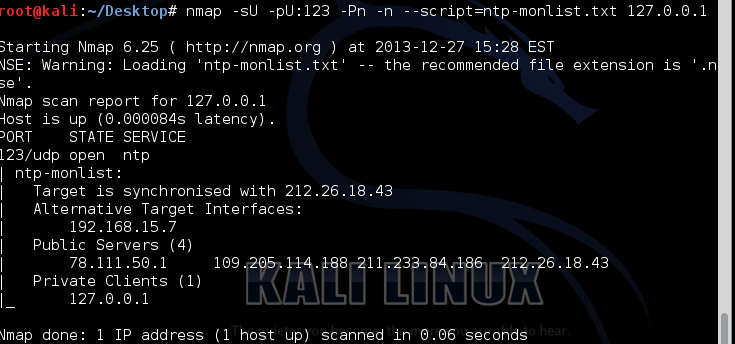
The Structure of Arpīelow listed fields are there in an ARP message. What is happening over here is that ARP request asks, “Can I have the MAC address”? And the reply is “Yes, you can”. When this ARP request message is received, the destination will automatically send back an ARP reply. So, after a host finds out the destination’s MAC address, an ARP request is sent out. Now, we get back to the problem statement, which says ‘the issue is there to find the destination MAC addressing’. In ARP, only two messages are defined – ARP request and ARP reply. ARP is built into every node of IP config, which means every system that is being developed on the IPV4 network has an ARP code included in it.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
